Amyloid and the Nervous System
- Hereditary ATTR (ATTRv) (FAP)
- Other types of hereditary amyloidosis.
- AL amyloidosis.
The normal nervous system?
- The brain and the spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS)
- The CNS interlinks with the peripheral nervous system, which through a network of nerve fibers sends messages around the body (hands and Feet etc.)
The peripheral nervous system has three main divisions: Autonomic, Sensory and Motor.
1) Autonomic Nerves:
- Essential for body’s involuntary movements.
- Connect to the internal organs
- Control blood pressure and heart rate, movements in the gut. digestion and bladder function.
- Carry information from the CNS to organs, glands and blood.
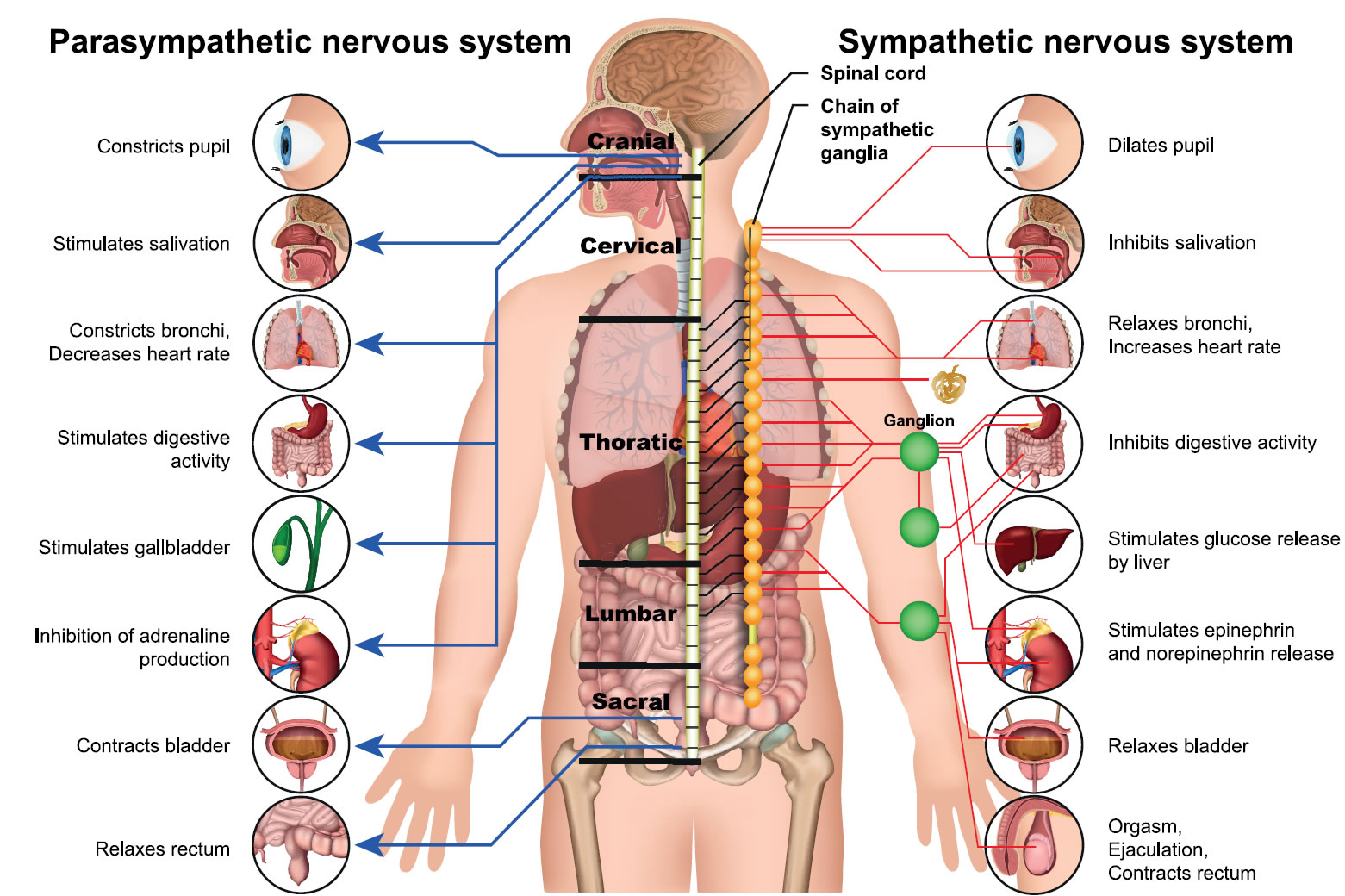
There are two types of autonomic nerves, the sympathetic and the parasympathetic.
- The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body for intense physical activity and is often referred to as the fight-or-flight response.
- The parasympathetic nervous system has almost the exact opposite effect and relaxes the body and inhibits or slows many high energy functions.
2) Sensory Nerves:
- Connect to the skin. Pass information from the sense receptors in the body, back to the CNS.
3) Motor Nerves
- Control the bodies voluntary movements.
- Send signals from the CNS to the skeletal muscles telling them when to relax or contract.
What happens when the amyloid protein deposits in the nervous system?
The amyloid proteins can deposit in the nerve fibers and around the nerves, gradually causing damage and interfering with the information sent between the brain and the organs through the autonomic nervous system.
This can result in what is known as peripheral and Autonomic Neuropathy.
N.B. Peripheral Neuropathy can also be caused by certain chemotherapy drugs but this usually resolves once the treatment has stopped.
Peripheral Neuropathy
There are three kinds of peripheral nerves.
- sensory nerves, which connect to the skin.
- motor nerves, which connect to the muscles.
- autonomic nerves, which connect to the internal organs.
All three kinds of peripheral nerves may be involved or just one.
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Neuropathy often interferes with the patient’s mobility and balance and may leave them wheel chair bound.
Numbness in the hands stops all fine movements which can impair self-care such as dressing and toileting.
Many patients and their families living with advanced neuropathy will experience anxiety, depression and loneliness.
Neuropathy in Amyloidosis – Symptoms & Management
A booklet from the Amyloidosis Research Consortium (ARC) – 2022
Carmel Woodrow: Peripheral Neuropathy
Professor Mary M. Reilly on Neuropathy in ATTR