Abstract
Background
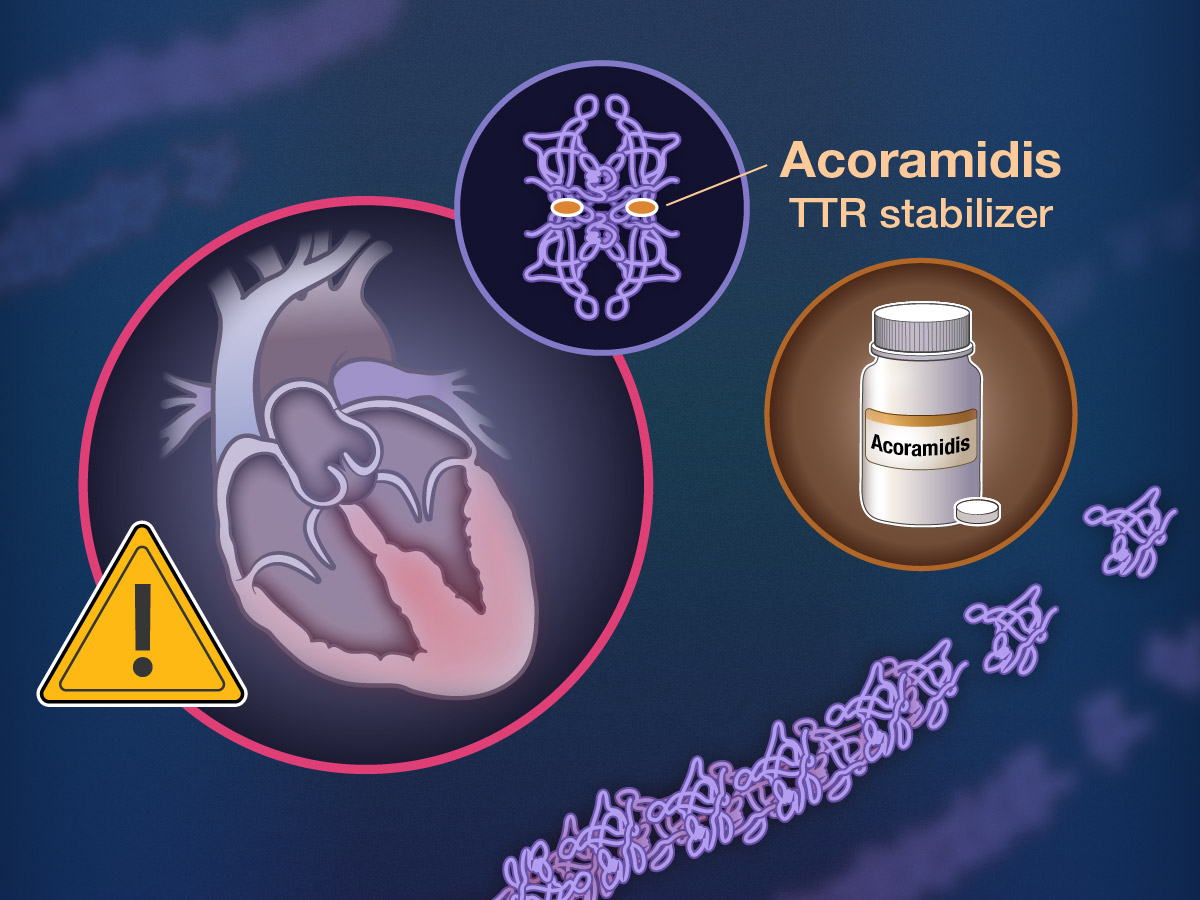
Transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy is characterized by the deposition of misfolded monomeric transthyretin (TTR) in the heart. Acoramidis is a high-affinity TTR stabilizer that acts to inhibit dissociation of tetrameric TTR and leads to more than 90% stabilization across the dosing interval as measured ex vivo.
Conclusions
In patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy, the receipt of acoramidis resulted in a significantly better four-step primary hierarchical outcome containing components of mortality, morbidity, and function than placebo. Adverse events were similar in the two groups.





